Vibrotherapy - supports the treatment of sciatica and lumbago
Vibrotherapy is effective in reducing pain sensation and associated disability in people suffering from chronic sacral pain radiating to the legs (sciatica, lumbago).
How does it work?
Wibracje znoszą ból na kilka sposobów: hamują neuronalne sygnały bólowe i łagodzą obrzęki zapalne mogące uciskać nerwy. Ponadto rozluźniają mięśnie, łagodząc ból mięśniowo-szkieletowy, spowodowany wysokim napięciem mięśni.

When and for whom?
Sciatica or lumbago are not disease entities, but are instead the consequence of a disorder related to the sciatic nerve. Irritation of the nerve causes acute pain, known as sciatica (ischialgia) or lumbago. The elderly are at risk of sciatica and lumbago, but so are young people, especially those who are physically active and work out, and do not warm up properly before exercising.
Effectiveness
Numerous studies show that vibrotherapy is an effective pain relief treatment for patients with lumbosacral back pain. Vibration stimulus has the best effect when applied precisely at the site of pain and administered at the correct frequency.

Lundeberg T, Nordemar R, Ottoson D. Pain alleviation by vibratory stimulation. Pain. 1984 Sep;20(1):25-44. doi: 10.1016/0304-3959(84)90808-X. PMID: 6333660.
Benefits of vibrotherapy

No side effects

Action confirmed by scientists and practitioners

Perceptible effects from 1 treatment

Long-lasting effects through systematic use
Choose the right product
We will help you select a set of modules that suits your conditions.
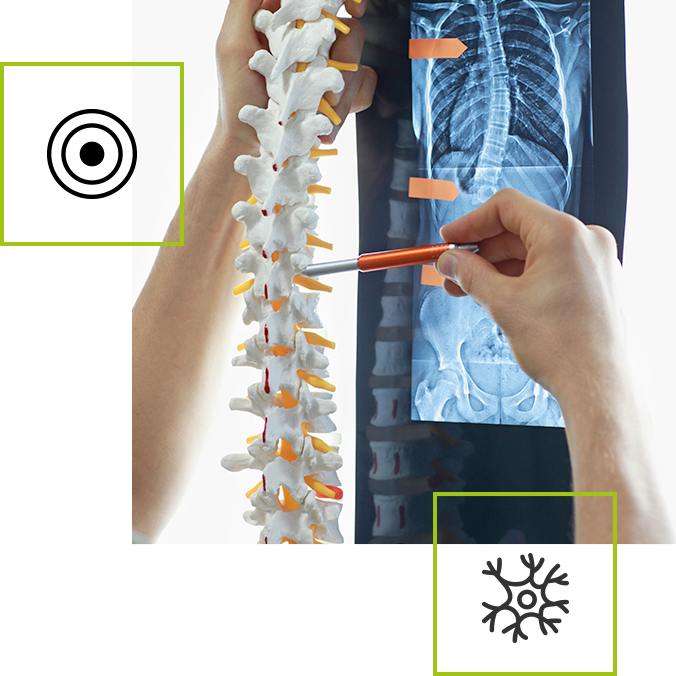
What is sciatica
Sciatica causes pain in the lumbar spine radiating into the legs. The cause of this condition (commonly referred to as a nerve root attack) is pressure on the sciatic nerve, consisting of the spinal nerves L4, L5 and S1. The pressure need not be directly on the sciatic nerve. More often, it results from pressure on the roots that make up this nerve, and pain information is transmitted to the spinal nerve. Sciatica occurs primarily as a result of a spinal disc (or more specifically, a herniated disc). Sciatica and radiating pain in the back and spine can also result from nerve irritation in the course of certain infectious diseases or local inflammation. The hallmark of sciatica is a strong muscle spasm leading to a twisting of the trunk.
Sciatica treatment
Symptoms of sciatica usually pass within 2 - 4 weeks of starting treatment. It is important to see a doctor or physiotherapist early on. Treatment of sciatica usually requires a combination of pharmacotherapy and physiotherapy. The use of painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs is necessary to treat the inflammation, while appropriate physical therapy allows pain relief and a return to fitness. During the treatment of sciatica, light and restful movement and activity matching the intensity of the pain is recommended. Total immobilisation of the patient is not advisable unless necessary. It is also important to prevent further inflammation, as the treatment of sciatica is a long-term process. It is always better to prevent than to treat sciatica. In everyday life, we can use simple methods to prevent unfavourable stresses and situations that exacerbate symptoms.
Sciatica causes
The most common causes of sciatica are pressure on the sciatic nerve roots in the spinal canal by the intervertebral disc. Stenosis (narrowing) of the spinal canal can also contribute to a sciatica attack. Pressure on the nerve can also occur as a result of increased tension of the gluteus medius muscle. This situation is called piriformis muscle syndrome, which can also trigger a sciatica attack. In rare cases, the pain that sciatica causes may be due to compression of the roots by abscessed lesions in the spinal canal or cancerous tumours. Sciatica also affects people with sedentary lifestyles, those who are obese, those who work physically and those who remain in a forced position for long periods of time. Pregnant women often complain of radiating pain in the lumbar spine.
Sciatica physiotherapy
Physiotherapy and rehabilitation are significant elements in the entire sciatica treatment process. They should not be put off or downplayed. Physical therapy treatments, such as vibrotherapy, are designed to reduce pain and improve the overall condition of the body in a non-invasive way. Physiotherapy and physical activity are also important in preventing sciatica recurrence. Adequate strengthening of the spinal muscles means that spinal pain radiating to the legs does not return. That's why it's so important to work on improving the condition of the lumbar spine on a daily basis. By taking care of the right sleeping position, physical activity tailored to one's abilities and daily hygiene, back pain will not bother us.
Sciatica symptoms
Sciatica most often takes the form of sharp pain radiating from the lumbar spine through the buttock, the back of the thigh to the toes. Radiation of pain to the limb is a characteristic symptom of sciatica. It may be accompanied by sensory disturbances, tingling, numbness or other neurological symptoms. Occasionally, there is also the appearance of muscle weakness in the painful leg or a slight paresis. The symptoms that sciatica gives most often affect one leg to which pain of varying intensity radiates. In rare cases, sciatica affects both limbs. It is most troublesome when standing up and changing positions. In addition, activities such as walking, coughing or even sneezing exacerbate the pain symptoms accompanying sciatica.
Sciatica and vibrotherapy
Vibrotherapy provides support for the treatment of sciatica through a variety of mechanisms. The vibrations generated during this therapy have the potential to relax tight muscles, which can provide relief and reduce the pain associated with sciatica. In addition, vibration helps to improve blood circulation, which is important for healing processes and reducing inflammation.
Stimulation of the nervous system by vibrotherapy can affect nerve reflexes, regulating nerve signals and reducing the excessive nerve reactivity associated with sciatica. The analgesic effect of vibration is also an important aspect, which can provide relief to patients suffering from pain associated with this condition.
Vibrotherapy can promote improved range of motion by improving muscle flexibility and also has a relaxing effect, contributing to the overall relief of muscle tension.






